Detecting mouse squamous cell carcinoma from submicron full‐field optical coherence tomography images by deep learning
Published in Journal of Biophotonics, 2020
Recommended citation: Chi-Jui Ho, Manuel Calderon‐Delgado, Chin‐Cheng Chan, Ming‐Yi Lin, Jeng‐Wei Tjiu, Sheng‐Lung Huang, and Homer H. Chen, "Detecting mouse squamous cell carcinoma from submicron full‐field optical coherence tomography images by deep learning," in Journal of Biophotonics, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/jbio.202000271
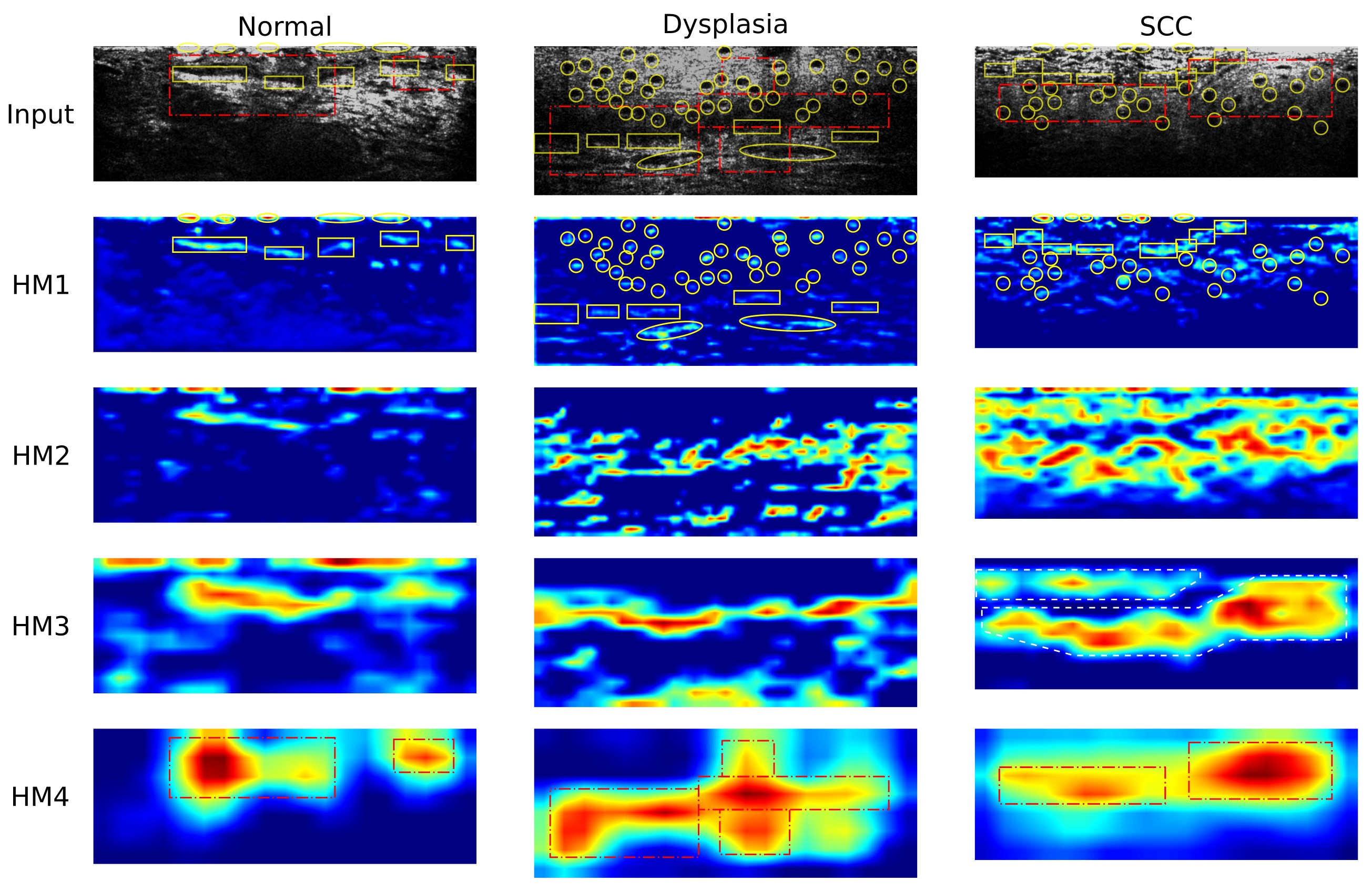
Abstract: The standard medical practice for cancer diagnosis requires histopathology, which is an invasive and time‐consuming procedure. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an alternative that is relatively fast, noninvasive, and able to capture three‐dimensional structures of epithelial tissue. Unlike most previous OCT systems, which cannot capture crucial cellular‐level information for squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) diagnosis, the full‐field OCT (FF‐OCT) technology used in this paper is able to produce images at sub‐micron resolution and thereby facilitates the development of a deep learning algorithm for SCC detection. Experimental results show that the SCC detection algorithm can achieve a classification accuracy of 80% for mouse skin. Using the sub‐micron FF‐OCT imaging system, the proposed SCC detection algorithm has the potential for in‐vivo applications.


